Heat shrink tubing is manufactured through a multi-step process to ensure durability and thermal responsiveness. Here’s an overview: The manufacturing process of heat shrink tubing involves material selection, extrusion, cross-linking, expansion, cutting, quality control, and packaging.
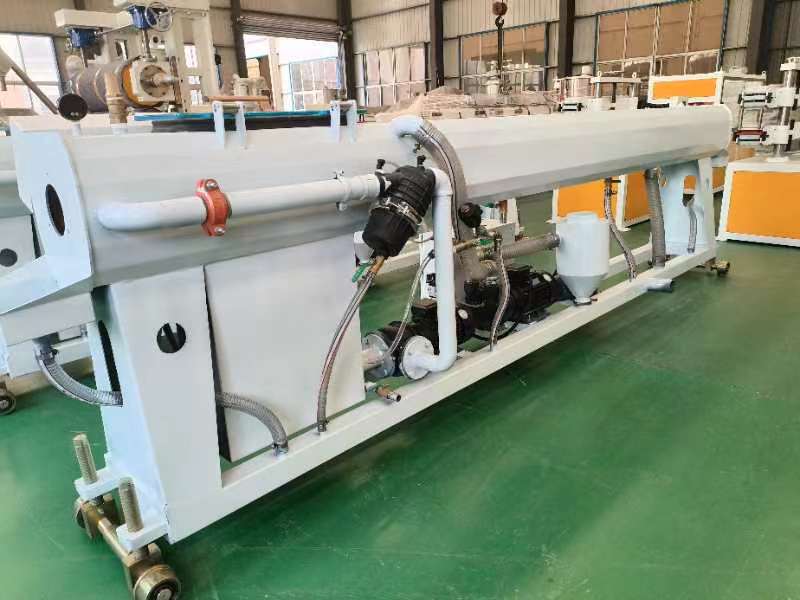
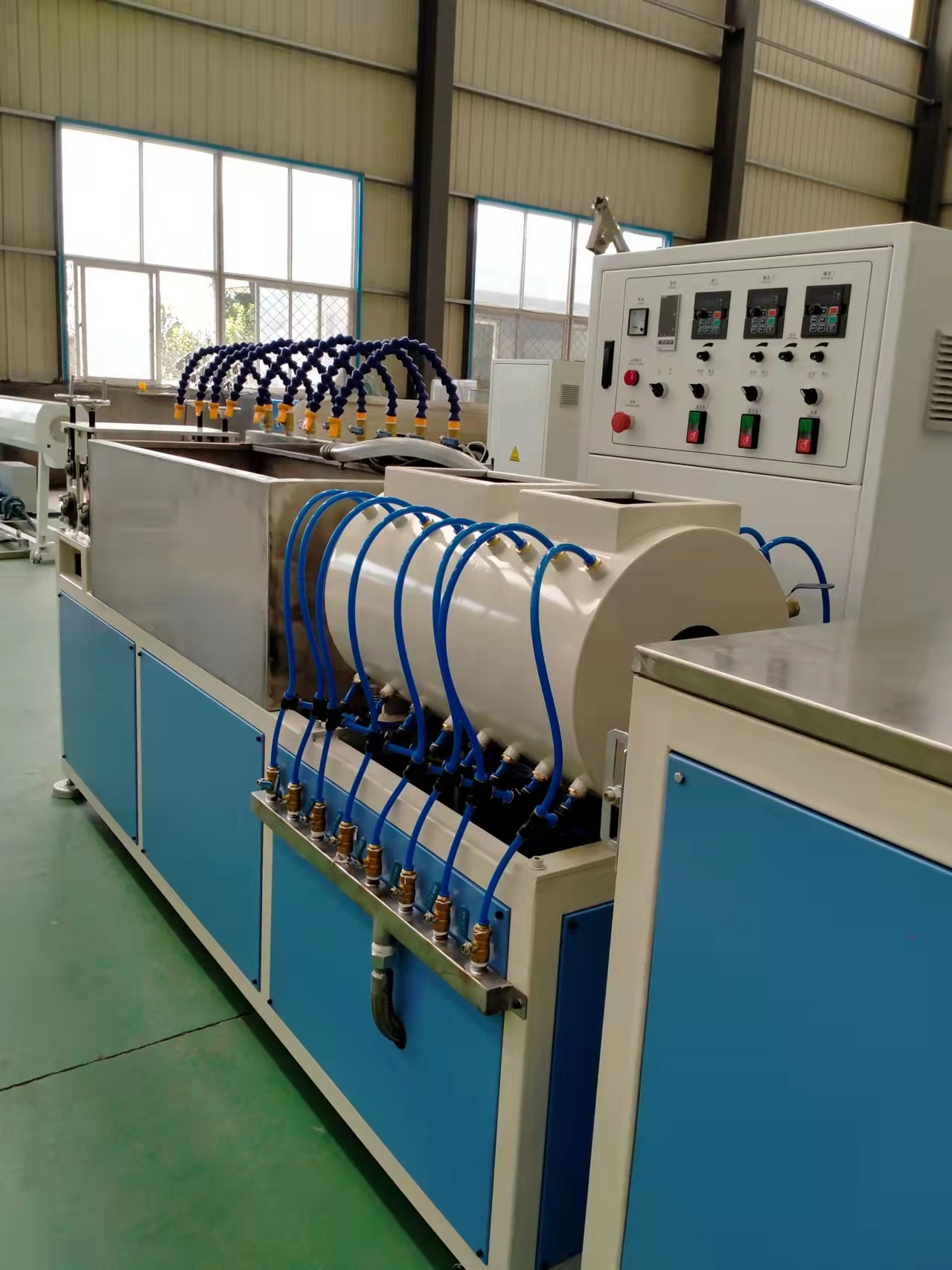
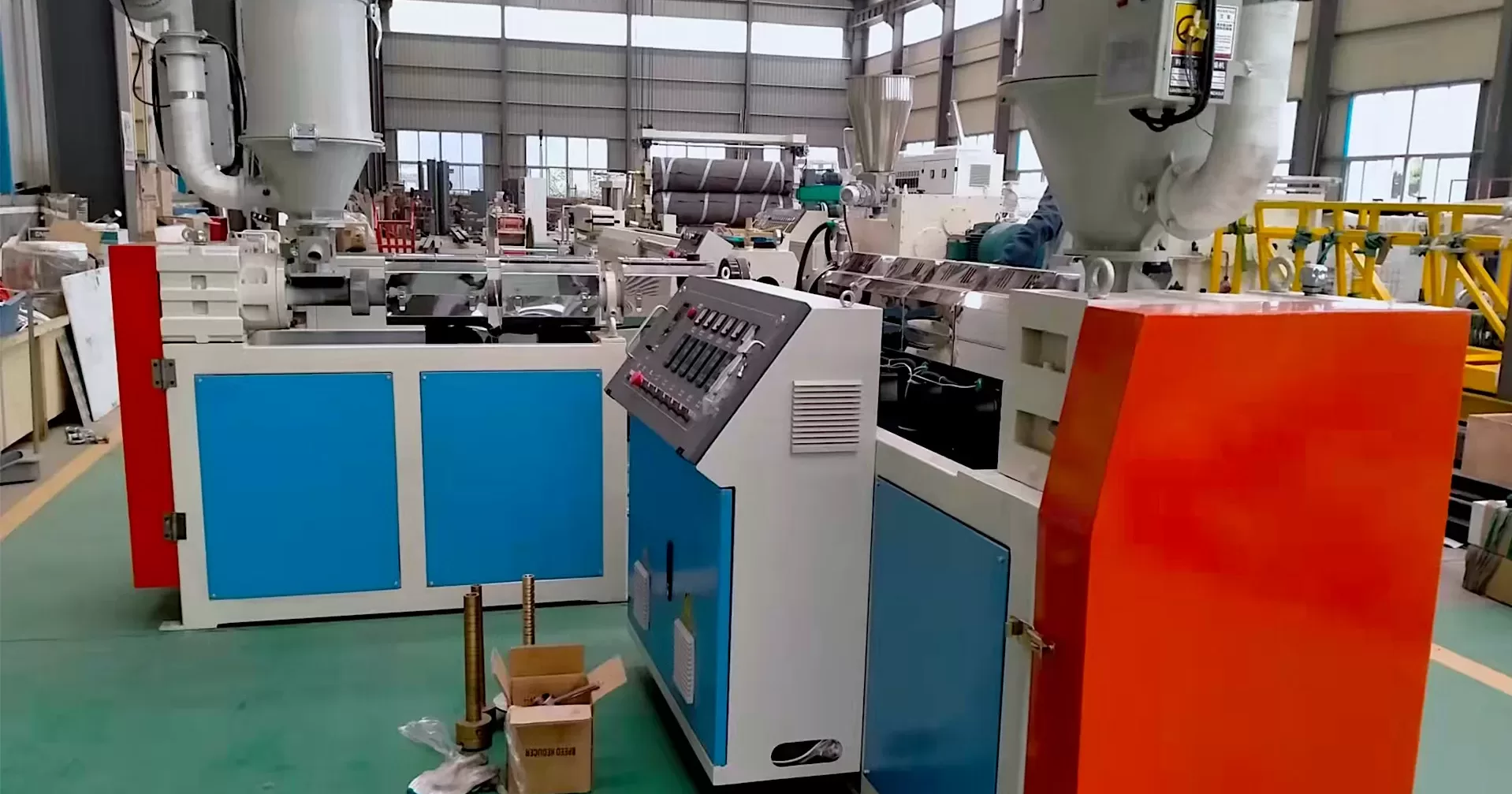
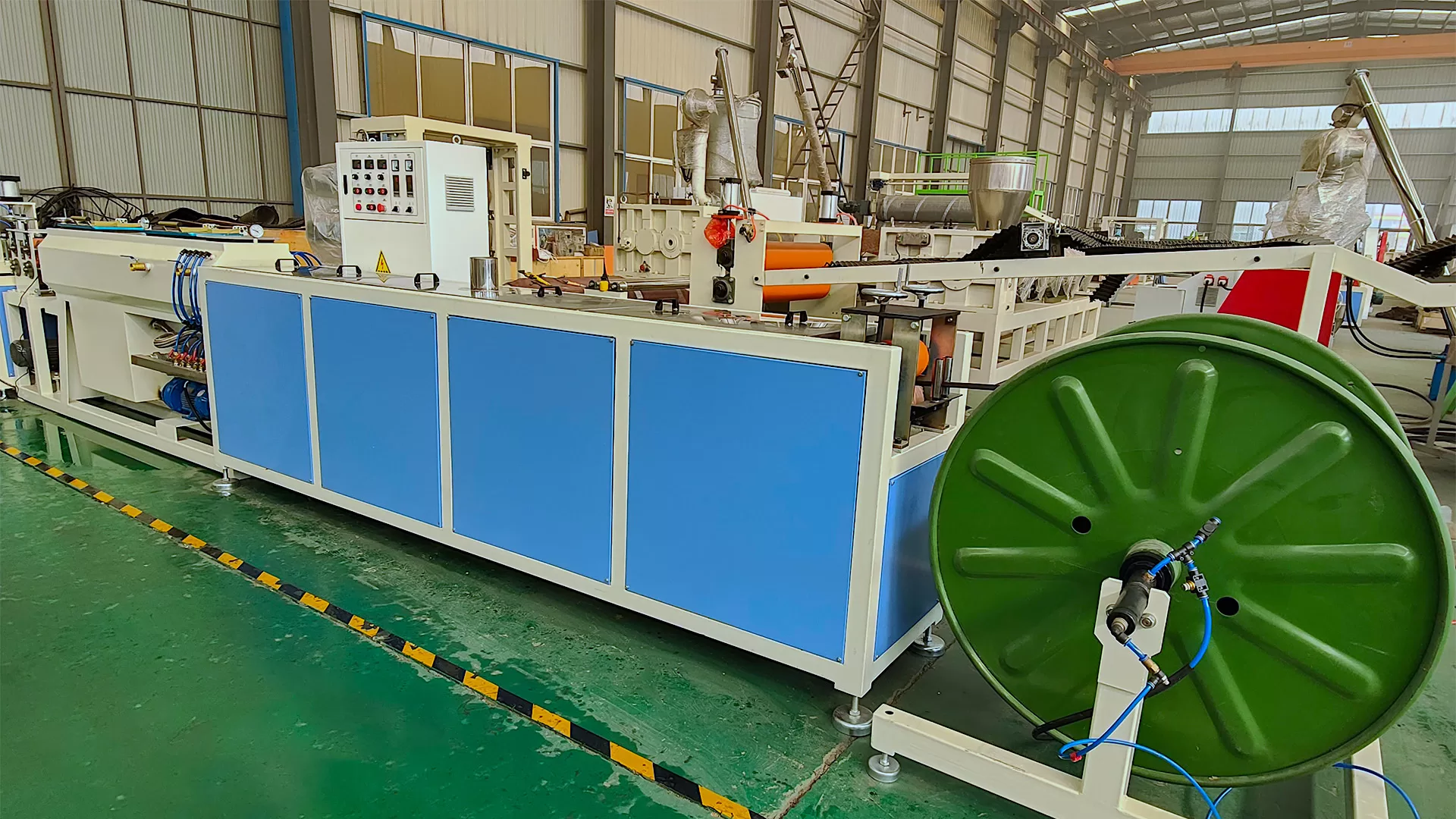
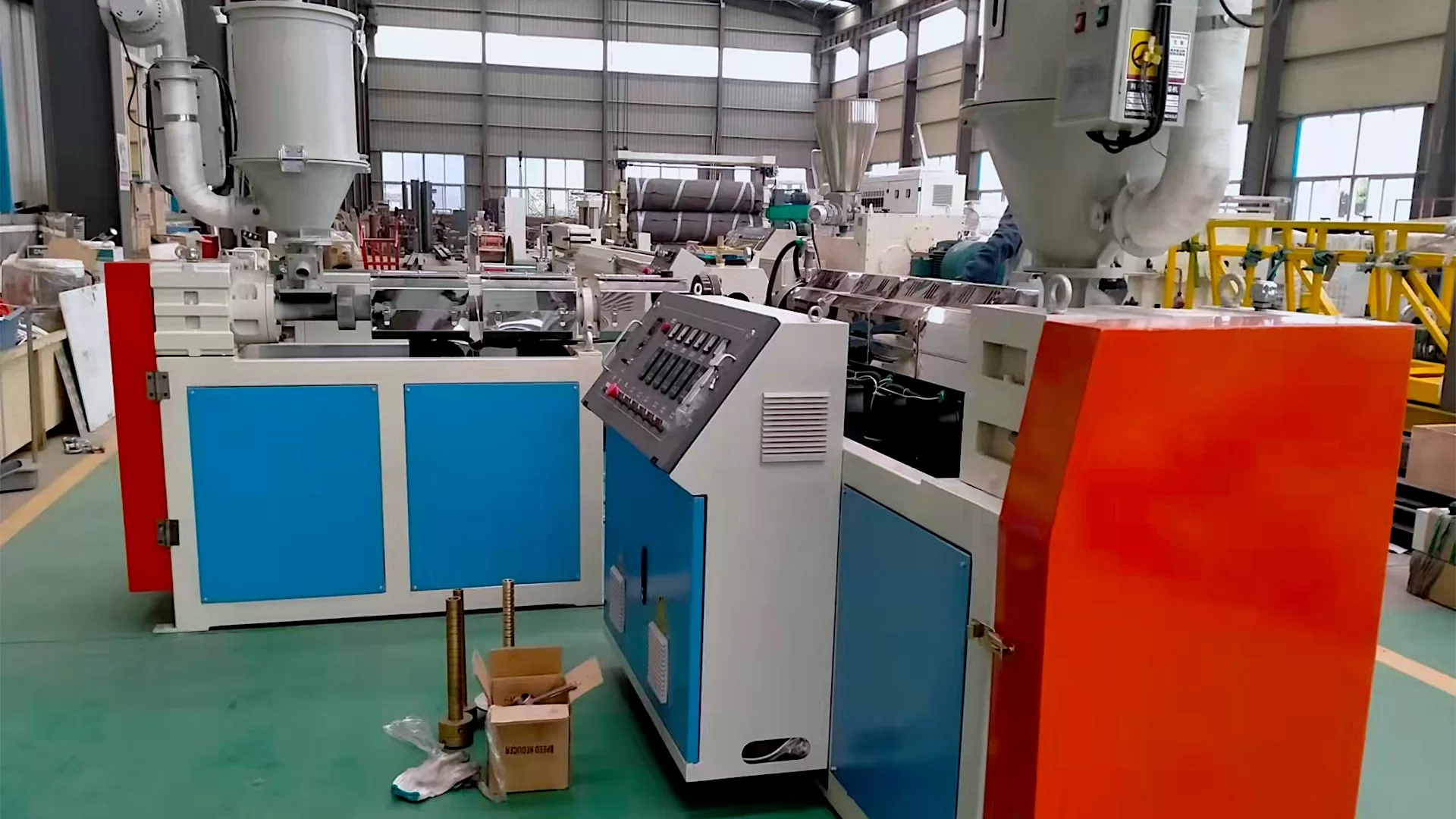
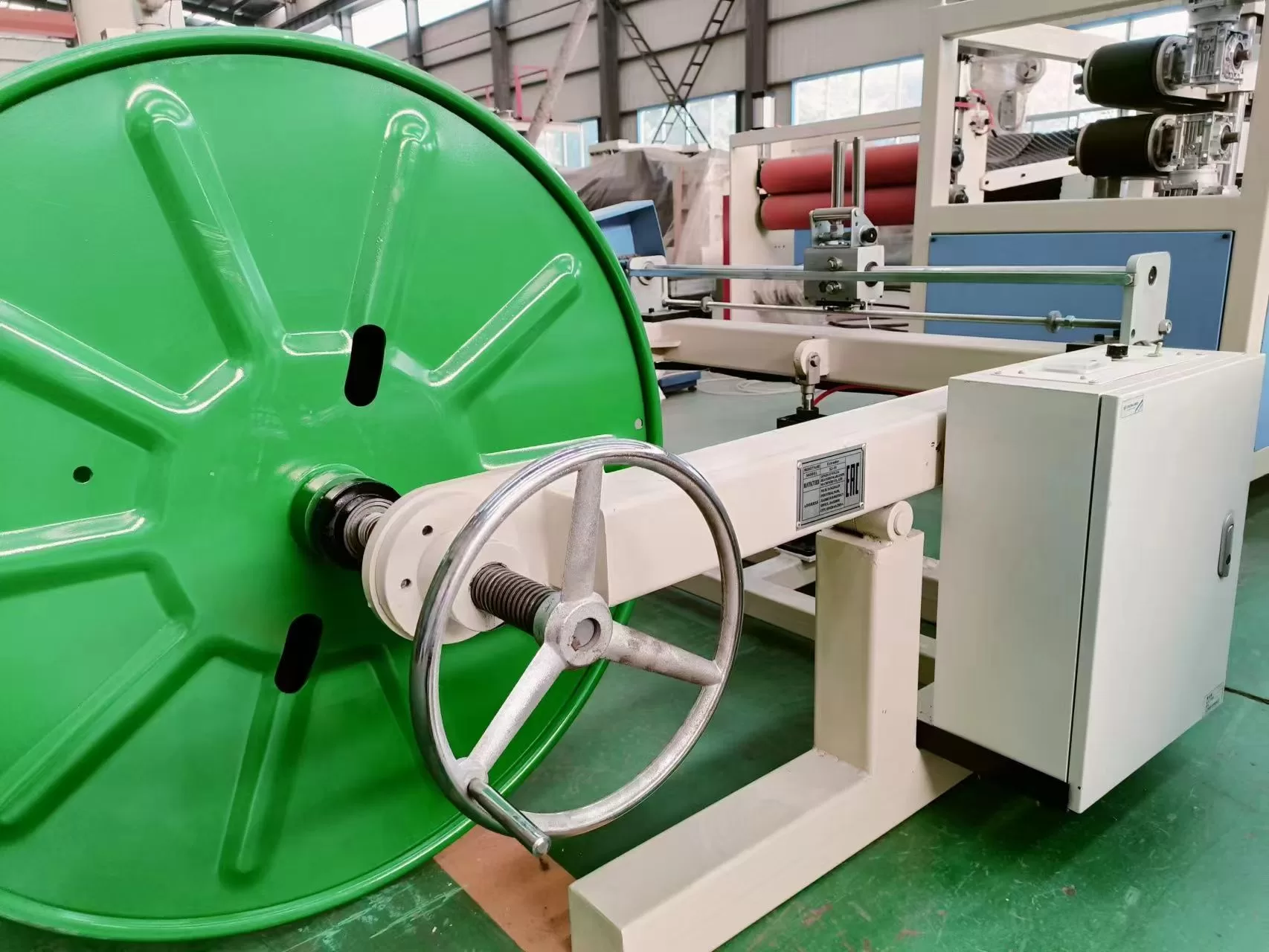
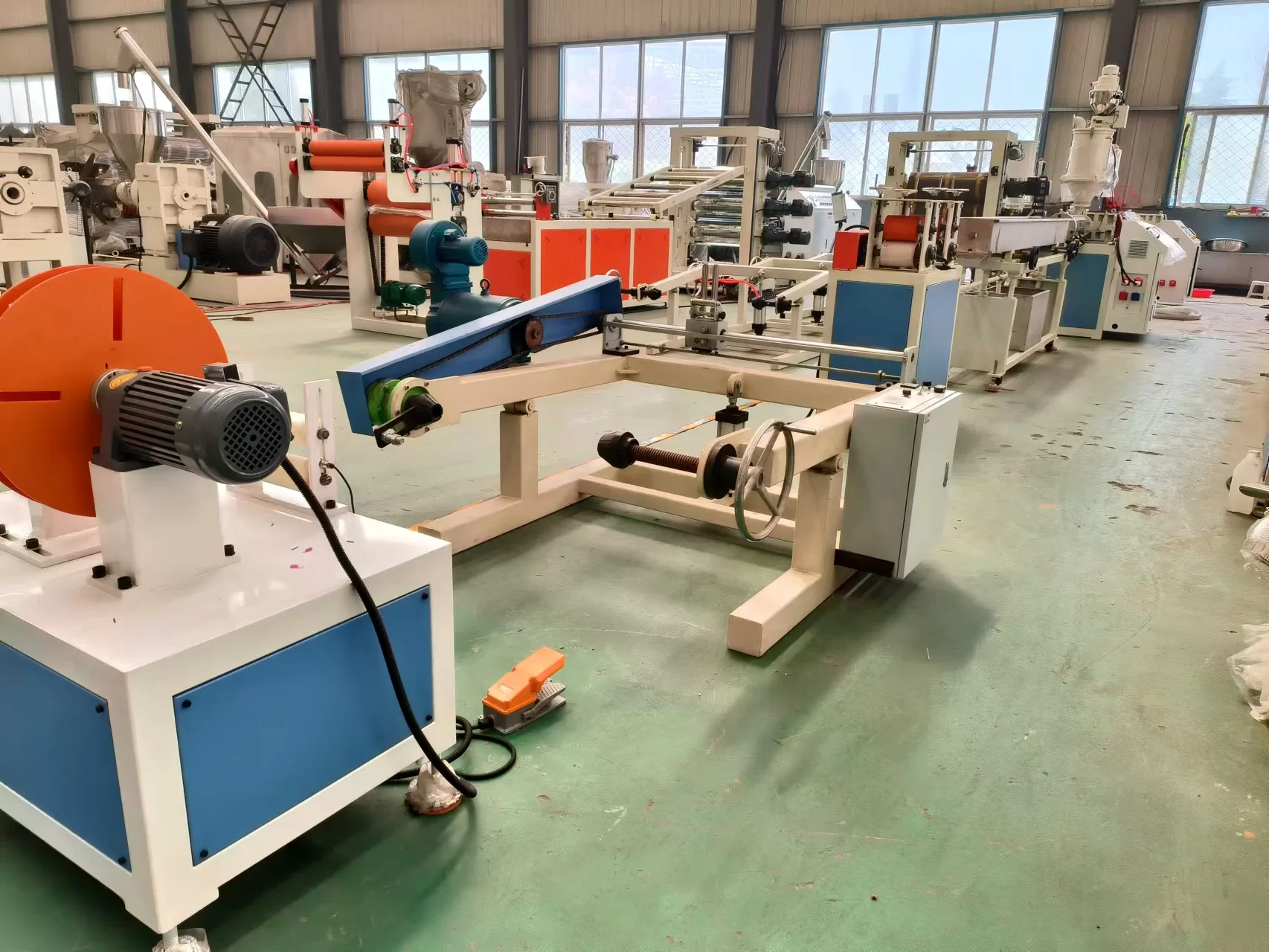








Material Selection: The process begins with choosing base polymers like polyethylene (PE), polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), or elastomers. Additives (e.g., stabilizers, colorants) are blended to enhance properties like UV resistance or flame retardancy.
Extrusion: The polymer mix is melted and extruded through a circular die to form a tube. Precise temperature control ensures uniform thickness and smooth surfaces. The extruded tube is cooled in water baths to solidify its initial shape.
Cross-Linking: To enable heat-shrink capabilities, the tubing undergoes cross-linking via electron beam irradiation or chemical methods. This creates molecular bonds, improving thermal stability and mechanical strength.
Expansion: The tube is reheated to a rubbery state and mechanically or pneumatically stretched to a larger diameter. It is then rapidly cooled (quenched) to “lock” the expanded shape.
Finishing: The tubing is cut to specified lengths, inspected for defects (e.g., dimensional accuracy, shrinkage ratio), and tested for electrical/mechanical performance. Surface printing or labeling may be added.
Packaging: Finished tubes are coiled or packed for shipment, often with anti-static or moisture-resistant measures.